Choosing Between LlamaIndex and LangChain
Building AI agents but not sure which of LlamaIndex and LangChain is a better option? You're not alone. Both frameworks have earned their stripes in production environments and are strongly supported in the open-source community.
But we find that it’s not always about choosing one over the other.

LlamaIndex and LangChain each bring unique strengths to the table. LangChain excels in building complex AI workflows with its modular architecture, while LlamaIndex specializes in efficient data retrieval and indexing across 160+ data sources. Many developers are finding that combining both can create more powerful applications than using either alone.
Overview
In this guide, we will explore:
- How LlamaIndex works
- How LangChain works
- Comparing learning curves
- Comparing performance
- Comparing multi-modal support
- How to combine both frameworks for your RAG applications
At a Glance
| LlamaIndex | LangChain | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | ✔ Data indexing and retrieval optimization | ✔ Building complex AI workflows |
| Key Strength | ✔ Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | ✔ Modular architecture for multi-step reasoning |
| Best For | ✔ Applications requiring efficient data processing from multiple sources | ✔ Prototyping and building end-to-end AI applications |
| Notable Feature | ✔ Supports 160+ formats (APIs, PDF, Documents, SQL, etc.) | ✔ Extensive integration options with various LLM models |
What is LlamaIndex?
LlamaIndex's focus on efficient data handling, indexing, and retrieval makes it particularly useful for applications that need to augment LLM responses with specific, domain-relevant information, effectively implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
How LlamaIndex Works
LlamaIndex has many available plugins you could load (or ingest) data from many sources easily, and generate vector embeddings using an embedding model.
One key feature of LlamaIndex is that it is optimized for index querying. After the data is ingested, an index is created. This index represents your vectorized data and can be easily queried like so:
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("How to build an AI agent?")
print(response)
LlamaIndex simplifies this process by taking your query "How to build an AI agent?" and matching it with the most relevant information from your vectorized data (or index). This information is then used as context for the LLM to generate a response. For more information on how to get started, check out LlamaIndex's documentation.
What is LangChain?
LangChain is a framework designed to facilitate LLM application development. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and components that allow developers to easily build, manage, and deploy LLM-powered applications.
How LangChain Works
Chains are key components of LangChain, allowing you to connect different components together to create complex workflows.
Prompt Template
A chain can include PromptTemplate, used to structure user input into a format that an LLM can process effectively. This involves defining templates with placeholders for dynamic content, which are filled in during runtime.
LLMChain
A chain can also include LLMChain, which is a component that combines an LLM with a prompt template. It takes the formatted input from the PromptTemplate, queries the LLM, and returns the result.
Here's an example of how these components work together:
# ... some code before
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=template, input_variables=["questions"])
chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt
)
chain.run(query)
Comparing Learning Curves
LangChain has a lower initial learning curve and is more intuitive for beginners. It offers more out-of-the-box components, extensive documentation and examples and a larger developer community with more resources. LlamaIndex is powerful but has a steeper learning curve compare to LangChain.
As you progress beyond the basics, LlamaIndex becomes more advantageous for specific tasks, particularly advanced RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) techniques. LangChain's extensive customizability can lead to a steeper learning curve if you are building advanced agents.
Comparing Performance
Both frameworks require careful consideration of performance factors for production environments. LangChain's issues stem from its complex architecture and resource management, while LlamaIndex's potential bottlenecks relate to its specialization and scalability constraints.
LlamaIndex
- Efficient for specific RAG tasks, limited flexibility for complex Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks.
- Performance tied to indexing efficiency.
- Requires scaling considerations for large datasets or high query volumes.
LangChain
- Complex architecture (multi-layered abstractions) requires careful management
- Abstraction = limited control over agent design
- Multiple API calls can impact latency (optimize API call frequency and implement caching)
- Resource usage like CPU usage and operational costs requires monitoring.
Comparing Multi-Modal Capabilities
LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex offers built-in support for multi-modal applications. It enables full multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines by supporting indexing and retrieving both text and image chunks within the same system. It also provides high-level abstractions to simplify building multi-modal RAG apps, like ready-to-use classes OpenAIMultiModal to easily integrate with models like GPT-4V.
LangChain
LangChain is primarily designed as a general-purpose framework for building LLM applications. Its core strengths lie in its tools for working with language models and text-based applications. While it can be used for multi-modal tasks, it doesn't have the same level of built-in support as LlamaIndex.
However, LangChain's flexible architecture allows for integration with external tools and models for multi-modal tasks. Developers may need to implement more custom logic for multi-modal applications.
LangChain and LlamaIndex, which is better for your use case?
Choose LlamaIndex when:
- Building RAG-focused applications
- Dealing with diverse data sources
- Requiring efficient data retrieval
- Working with multi-modal data
Choose LangChain when:
- Creating complex AI workflows
- Building end-to-end applications
- Needing extensive LLM integration
- Requiring agent-based systems
Use both when:
- Building data-intensive applications with complex workflows
- Requiring both efficient retrieval and sophisticated processing
- Implementing multi-modal applications with complex reasoning
(Short) Elevator Pitch :)
Building multi-step agents can be tricky, especially when an error in one part of the chain affects the entire outcome. Helicone’s observability dashboard and Sessions feature (that comes with the Pro plan) can help you identify precisely where the breakdown occurs, enabling faster troubleshooting.
Using Both LlamaIndex and LangChain
LangChain and LlamaIndex can be used together to make your RAG application more powerful.
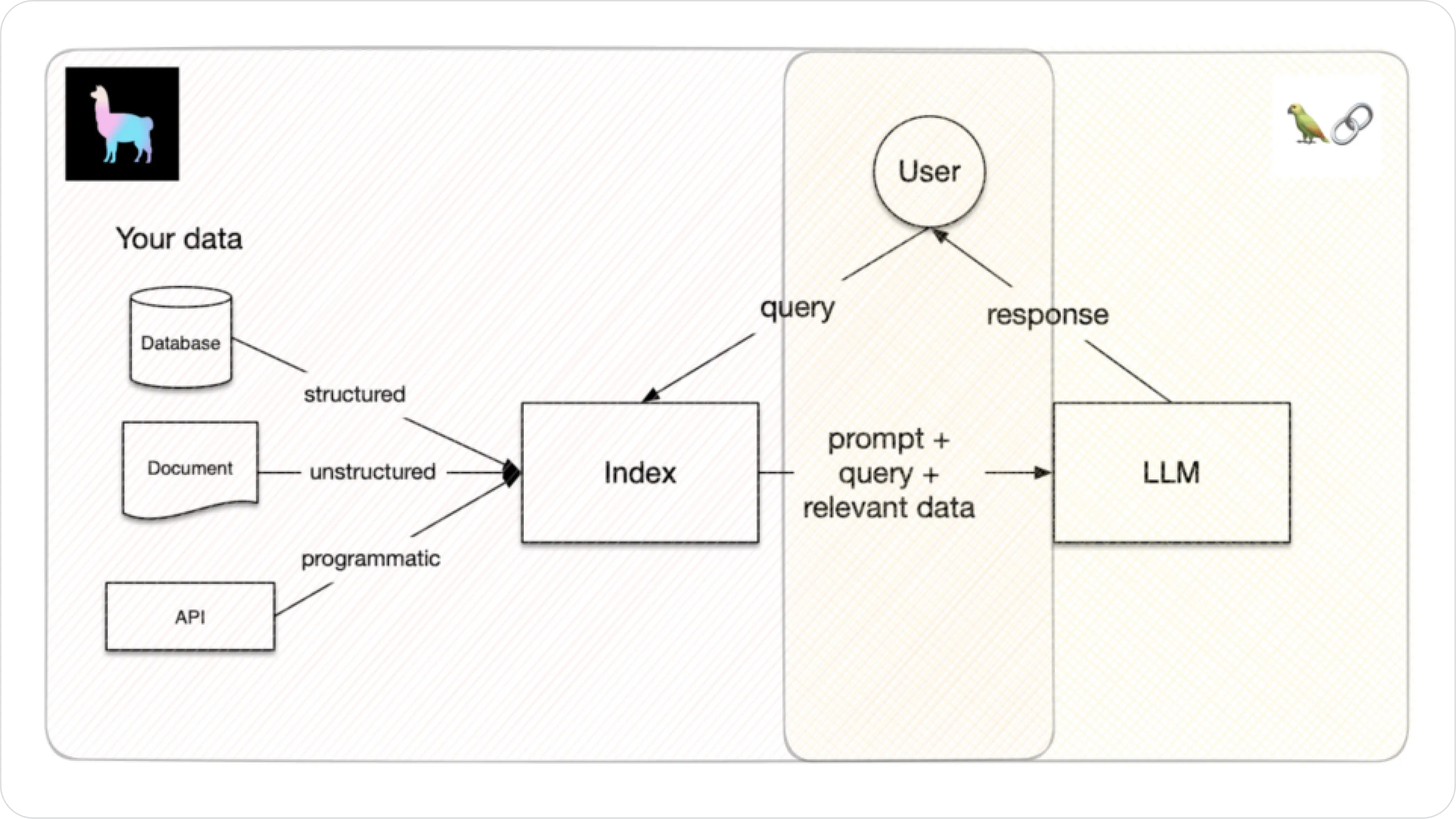 Image: LlamaIndex vs LangChain: Understand the Key Differences
Image: LlamaIndex vs LangChain: Understand the Key Differences
Combined Approach
(Data Layer) Use LlamaIndex as a LangChain tool for:
- Efficient data indexing
- Optimized retrieval systems
- Multi-modal data handling
(Application Layer) Use LangChain for:
- Complex workflow management
- Agent-based systems
- Multi-step reasoning
Implementation Example
# LlamaIndex as a LangChain tool
from llama_index.core.langchain_helpers.agents import (
IndexToolConfig,
LlamaIndexTool,
)
tool_config = IndexToolConfig(
query_engine=query_engine,
name="Vector Index",
description="useful for when you want to answer queries about X",
tool_kwargs={"return_direct": True},
)
tool = LlamaIndexTool.from_tool_config(tool_config)
Bottom Line
LangChain is a good option if you need quick prototyping and flexibility or complex reasoning tasks. LlamaIndex is ideal if your focus is primarily on data retrieval. If you’re building enterprise applications, consider using both frameworks together, while implementing proper monitoring and optimization.
You might find these useful:
- 6 Awesome Frameworks for Building AI Agents (Open-Source)
- Debugging RAG Chatbots and AI Agents with Sessions
- How Replaying LLM Sessions Enhances Performance
Questions or feedback?
Are the information out of date? Do you have additional platforms to add? Please raise an issue and we’d love to share your insights!